Motor Applications

Can an AC stepping motor be used in robotics applications ?
AC stepping motors can be used in robotics applications, offering precise control and high torque. However, they have speed limitations and can overheat, requiring cooling mechanisms. Consider application requirements and compatibility with control systems before choosing an AC stepping motor for a robotic project.

How does a single motor drive compare to a dual motor drive ?
This article compares single motor drives and dual motor drives based on their performance, efficiency, cost, and applications. Single motor drives can only control one motor at a time, while dual motor drives can control two motors simultaneously. Dual motor drives offer higher overall torque and better synchronization between multiple motors, but they also consume more power and require more maintenance. Single motor drives are typically less expensive and well-suited for low power applications with simple movement profiles, while dual motor drives are appropriate for high power applications with complex movement profiles requiring precise synchronization. The choice between a single motor drive and a dual motor drive depends on the specific requirements of the application.

Can you provide some examples of applications where multi-motor drives are used ?
Multi-motor drives are used in various applications where multiple motors need to be controlled simultaneously, including industrial automation, CNC machines, electric vehicles, wind turbines, robotics, and aerospace.

Can a DC brushed motor be used for high-power applications such as electric vehicles or aircraft ?
DC brushed motors have advantages such as simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. However, they face challenges in high-power applications like electric vehicles or aircraft due to limited power output, efficiency issues, and maintenance concerns. Alternatives like brushless motors and switched reluctance motors are better suited for these scenarios due to their higher power density, improved efficiency, and reduced maintenance requirements.
What is the difference between single motor and multi-motor drives ?
Single motor drives control only one motor and are simple, cost-effective, and easy to maintain. Multi-motor drives control multiple motors simultaneously and offer increased flexibility, improved performance, and enhanced functionality but are more complex and expensive. The choice between these two types of drives depends on the specific requirements of the application.

Are there any drawbacks to using permanent magnet motors in certain applications ?
The text discusses the drawbacks of using permanent magnet motors in certain applications, including high cost, demagnetization risk, limited speed range, difficulty in controlling torque and speed, and sensitivity to heat and vibration. These factors make them less suitable for applications where cost is a primary concern, precise control is necessary, or exposure to high temperatures or vibrations is common.

What are some common applications for brushless motors ?
Brushless motors, also known as BLDC (Brushless Direct Current) motors, are becoming increasingly popular due to their efficiency, reliability, and performance. Here are some common applications for brushless motors: 1. Electric Vehicles and Scooters 2. Drones and Quadcopters 3. Model Airplanes and RC Cars 4. Industrial Applications 5. Appliances and Tools 6. Aerospace and Defense 7. Medical Devices 8. Marine Applications 9. Renewable Energy

What is a hub motor ?
A hub motor is an electric motor integrated into a vehicle's wheel hub, offering direct drive, simplified design, quiet operation, and space efficiency. However, it has limitations such as limited power output, overheating concerns, and cost considerations. Hub motors are commonly used in electric vehicles like bicycles, scooters, motorcycles, and cars.

In what applications is a single motor drive commonly used ?
Single motor drives are used in various applications for precise control of speed, torque, and position. These applications include industrial automation (robotics, conveyor systems, packaging machines), transportation (EVs, hybrid vehicles, drones), home appliances (washing machines, dishwashers, refrigerators), HVAC systems (air conditioners, heat pumps, ventilation systems), and agriculture (irrigation systems, farm equipment, greenhouses).
What is an internal rotor motor ?
The text discusses the design, advantages, disadvantages, and applications of internal rotor motors. Internal rotor motors are a type of electric motor where the moving part (rotor) is inside the stationary part (stator). They offer benefits such as high efficiency, good heat dissipation, simplicity in construction, and low inertia. However, they also have limitations like limited torque density, difficulty in cooling, and potential for magnetic saturation. These motors are commonly used in automotive, aerospace, industrial equipment, and consumer electronics applications.

What are the benefits of using a combination motor drive system ?
Combination motor drive systems offer benefits such as improved efficiency, increased reliability, flexibility, and enhanced control. These systems combine the advantages of different types of motors to create a more efficient and reliable drive system. They are ideal for a wide range of applications and can help businesses save money on energy costs while reducing downtime and maintenance requirements.

What are the advantages of using a brushless motor ?
Brushless motors offer several advantages over traditional brushed motors, including higher efficiency, longer lifespan, improved performance, quieter operation, enhanced reliability, and environmental benefits. These benefits make them an attractive choice for a wide range of applications.
What are the different types of combination motor drives available in the market ?
The article discusses different types of combination motor drives, including AC, DC, servo, and stepper motor drives. It highlights their unique features such as precise speed control, high torque output, regenerative braking, position control, feedback systems, and microstepping capabilities. The article emphasizes the importance of selecting the appropriate type of motor drive based on the specific needs and requirements of the application.
What are the advantages of using a single motor drive system ?
A single motor drive system is a type of electric motor control system that uses only one motor to power a machine or equipment. This system has several advantages over other types of drive systems, including simplified design and maintenance, improved efficiency and performance, increased reliability and longevity, and greater flexibility and versatility. These benefits make it an attractive option for many industrial applications where precise control and efficient operation are essential.

How does the design of a permanent magnet motor differ from an induction motor ?
The article discusses the differences between permanent magnet motor and induction motor design, focusing on three main aspects: rotor design, stator winding design, and cooling system. The rotor of a permanent magnet motor contains high-energy rare-earth magnets that interact with the stator windings to produce torque, while the rotor of an induction motor has aluminum or copper bars that induce currents when exposed to a rotating magnetic field produced by the stator windings. The stator winding design also varies between the two types of motors, with permanent magnet motors typically having a three-phase distributed winding and induction motors having either a distributed or concentrated winding. Finally, the cooling system design differs as well, with permanent magnet motors often relying on natural convection or forced air cooling, while induction motors may use external fans or blowers for more effective heat removal. Understanding these differences is crucial for engineers to choose the appropriate motor type for their needs and optimize its performance accordingly.
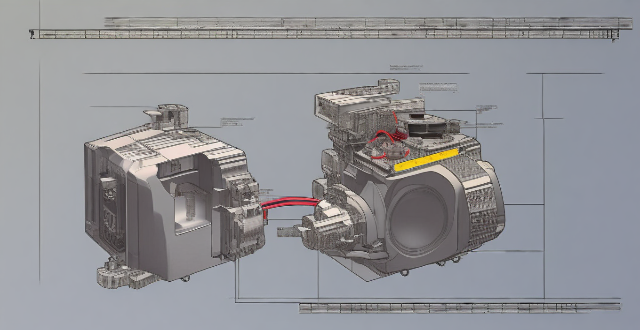
What are the advantages of using an internal rotor motor ?
An internal rotor motor is a type of electric motor where the rotor is located inside the stator. This design has several advantages over other types of motors, such as external rotor motors or brushed motors. Some of these advantages include higher efficiency, improved heat dissipation, lower noise levels, better control and response, compact design, and reduced maintenance costs. These benefits make internal rotor motors a popular choice for various applications across industries.
How does a multi-motor drive system work ?
The text explains how a multi-motor drive system works, its components, and benefits. It describes the process of power conversion, control signals, motor operation, mechanical transmission, and feedback adjustment in such systems. The advantages include improved efficiency, increased redundancy, and enhanced control.

How much power can a hub motor generate ?
Hub motors are electric motors built into the wheel's hub and are commonly found in electric vehicles, wheelchairs, and other space-limited applications. The power generation of a hub motor is influenced by its design, size, and the type of battery it uses. Larger motors generally produce more power but require more energy to operate. The control system managing the motor's power output can also affect performance. Examples of hub motor power generation include small electric bikes (250-500 watts), medium electric bikes (500-1000 watts), large electric bikes (over 1000 watts), electric wheelchairs (250-1000 watts), and other applications like golf carts and electric cars with varying power ratings.
How do I choose the right drive motor for my application ?
When selecting a drive motor for your application, considerWhen selecting a drive motor for your application, considerrque and speed, power duty cycle, cost, size, control compatibility, safety compliance, maintenance, and manufacturer reputation. This comprehensive guide helps ensure you choose a motor that meets your needs effectively and efficiently.

How do you choose the right AC stepping motor for your project ?
Choosing the right AC stepping motor requires understanding project needs, selecting the appropriate motor type, ensuring compatibility with control systems, considering physical constraints, evaluating performance characteristics, accounting for environmental factors, managing budgetary considerations, relying on supplier support and reputation, and conducting thorough testing.

What is the typical cost difference between a permanent magnet motor and an equivalent size induction motor ?
Permanent magnet motors (PMMs) and induction motors (IMs) are two common types of electric motors used in various applications. The cost difference between them is often a significant factor in deciding which one to use. PMMs are known for their high efficiency, compact size, and low noise levels, while IMs are simpler and more robust. The cost difference depends on factors such as size, power rating, materials used, and manufacturing processes. Generally, PMMs are more expensive than IMs of equivalent size due to material costs, manufacturing processes, efficiency and performance requirements, and market demand and availability. When choosing between these two types of motors, it is essential to consider both the technical requirements and budget constraints of your specific application.

What is a brushless motor ?
Brushless motors, also known as BLDC (Brushless Direct Current) motors, are electric motors that use an electronic controller to switch the current in their stator windings. They have higher efficiency, longer lifespan, higher power density, lower maintenance requirements, and quieter operation compared to brushed motors. The working principle of a brushless motor involves three main components: the rotor, stator, and electronic controller. Brushless motors are used in various applications, including aircraft, automotive, appliances, and industrial equipment.

What is an AC stepping motor and how does it work ?
An AC stepping motor is a type of electric motor that operates on alternating current and moves in discrete steps. It is commonly used in applications requiring precise control, such as robotics, CNC machines, 3D printers, and automation systems. The motor's movement is achieved by energizing its coils in a specific sequence, causing the rotor to turn a fixed angle for each step. The components of an AC stepping motor include the stator, rotor, and drive system. The stator is the stationary part of the motor containing coils or windings. The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, which has magnetic teeth. The drive system controls the sequence and timing of electrical pulses sent to the stator coils. The operational principle of an AC stepping motor involves winding energization, rotor alignment, stepping action, and repeating sequence. When an electrical current is applied to the stator windings, it creates a magnetic field. The magnetic field interacts with the rotor's magnetic teeth, causing them to align with the stator's field. By changing the sequence of the energized coils, the rotor is forced to rotate to a new position where the teeth again align with the stator's magnetic field. Continuously changing the energized coils causes the rotor to move in a series of small steps. There are two phases of operation for an AC stepping motor: single phase and multi-phase. Single phase operates using only one phase of AC power, typically for simpler applications. Multi-phase uses multiple phases of AC power for more complex movements and higher torque requirements. Control and drive systems for an AC stepping motor include microstepping, drivers, and controllers. Microstepping allows the motor to move in even smaller steps than its inherent step angle by controlling the current through the windings. The driver translates digital commands into the appropriate current levels and patterns required by the motor. The controller sends commands to the driver based on input from sensors or user interfaces. Advantages of an AC stepping motor include precision, simple control, and high reliability. Disadvantages include low top speed, resonance issues, and torque drop-off. In summary, an AC stepping motor converts electrical pulses into discrete mechanical movements through the interaction of its stator and rotor components. Its operational simplicity and precision make it ideal for various control applications despite some limitations in speed and resonance concerns.

What are the advantages of using an AC stepping motor compared to a DC stepping motor ?
The text discusses the advantages of using AC stepping motors compared to DC stepping motors. The main points include: 1. **Simplified Drive Circuitry**: AC stepping motors have simpler drive circuitry than DC stepping motors, leading to fewer components and a more streamlined design, which reduces complexity and lowers manufacturing costs. 2. **Higher Torque Output**: AC stepping motors typically offer higher torque output than DC stepping motors, making them ideal for applications requiring high torque at low speeds. This also leads to improved efficiency and reduced energy consumption. 3. **Better Heat Dissipation**: AC stepping motors often have better heat dissipation capabilities due to their larger surface area and improved cooling mechanisms, allowing them to operate at higher temperatures without overheating and extending their lifespan. 4. **Compatibility with Standard AC Power Sources**: AC stepping motors are compatible with standard AC power sources widely available in industrial and commercial settings, eliminating the need for additional power supplies or conversion equipment and simplifying installation. 5. **Lower Maintenance Requirements**: AC stepping motors generally require less maintenance than DC stepping motors, as they have fewer moving parts and simpler drive circuitry, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. Overall, the text highlights that AC stepping motors offer significant benefits over DC stepping motors in terms of simplicity, performance, efficiency, compatibility, and maintenance, making them a popular choice for various applications where precision control and reliability are essential.
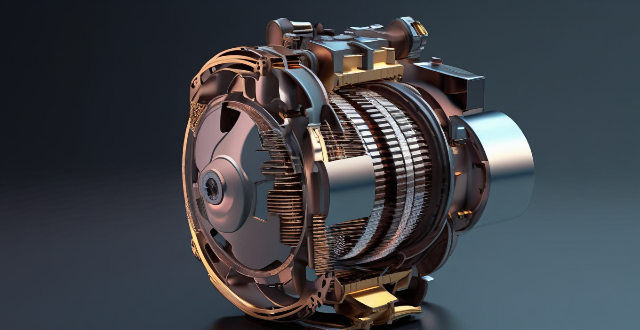
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a combination motor drive compared to a single motor drive ?
The combination motor drive has several advantages over a single motor drive, including improved performance, enhanced reliability, flexibility in design, energy efficiency, and modularity and scalability. However, it also has disadvantages such as complexity, cost, space requirements, synchronization issues, and integration challenges.

Can a single motor drive be used for heavy-duty tasks ?
A single motor drive can indeed be used for heavy-duty tasks, but it depends on several factors such as the type of motor, its power rating, and the nature of the task. There are various types of motors available, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The power rating of a motor is an important factor to consider when determining whether it can handle heavy-duty tasks. The nature of the task is another critical factor to consider. By carefully considering these factors and choosing the right motor for the job, you can ensure that your system is reliable, efficient, and effective.

What are the advantages and disadvantages of using a DC brushed motor in robotics ?
DC brushed motors in robotics offer advantages such as affordability, simple maintenance, and high-speed efficiency. They provide predictable behavior and quick response to voltage changes, making them suitable for tasks requiring fast movements. However, they also present disadvantages including limited lifespan due to commutator wear, overheating issues, reduced torque at low speeds, electrical noise leading to EMI/RFI, higher power consumption, and potential size and weight constraints. The decision to use a brushed or brushless motor depends on the specific requirements of the robotic application.

Can you explain the concept of vector control in multi-motor drives ?
Vector control is a method for controlling the speed and torque of electric motors, especially AC motors, in multi-motor drives. It works by decoupling the flux-producing and torque-producing components of the stator current, allowing for independent control of both. This results in improved dynamic response, precise speed regulation, energy efficiency, reduced mechanical stress, and adaptability to different motor types.

Can you explain the differences between an internal and external rotor motor ?
Motors are crucial components of various mechanical systems, and understanding their types is essential for selecting the appropriate one for a specific application. Two common types of motors are internal rotor motors and external rotor motors. An internal rotor motor has its rotor located inside the stator, while an external rotor motor has its rotor located outside the stator. The main differences between these two types of motors include rotor location, torque output, cooling efficiency, maintenance accessibility, and application suitability. Understanding these differences can help in selecting the appropriate motor type for a given task.

How can I choose the right combination motor drive for my application ?
When selecting a combination motor drive for your application, consider factors such as the type of motor (AC, DC, stepper, or servo), application requirements (load characteristics, speed and torque needs, control precision), appropriate drive technology (VFDs, electronic speed controls, stepper motor drives, servo amplifiers), compatibility and integration with existing systems, performance features (efficiency, dynamic response, protection features), budget and cost considerations (initial and operating costs), and seek professional advice from manufacturers and technical support.