Device Booster

Will a signal booster work with all types of devices ?
A signal booster is designed to improve the strength and reliability of wireless signals, such as cellular, Wi-Fi, or radio frequencies. However, whether a signal booster will work with all types of devices depends on several factors, including the compatibility of the booster with the device's technology and frequency bands. Compatibility: Cellular Networks: Signal boosters for cellular networks are typically designed to work with specific frequency bands used by different mobile operators. For example, a booster that supports 2G, 3G, and 4G LTE signals may not be compatible with 5G networks unless it explicitly states so. Therefore, it's essential to check the specifications of both your device and the booster to ensure they are compatible. Wi-Fi Networks: Wi-Fi signal boosters, also known as Wi-Fi extenders or repeaters, are designed to work with standard Wi-Fi protocols like 802.11b/g/n/ac/ax. Most modern devices support these standards, but older devices may not be compatible with newer protocols like 802.11ac or 802.11ax. Additionally, some boosters may only support single-band operation (2.4 GHz) while others offer dual-band (2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) support, which can affect compatibility with your device. Radio Frequencies: For other types of radio signals, such as walkie-talkies or CB radios, boosters must be designed to operate at the correct frequency. These boosters are often more specialized and less universal than those for cellular or Wi-Fi networks. It's crucial to match the booster's frequency range with the frequency your device uses. Installation and Placement: Even if a signal booster is technically compatible with your device, its effectiveness can be influenced by proper installation and placement. Here are some key considerations: Location of the Booster: The booster should be placed in an area where it can receive a strong signal from the source (e.g., a cell tower or router) and then amplify it for your device(s). Cable Quality and Length: If using a wired connection between the booster and your device or router, make sure to use high-quality cables that are not too long, as this can degrade signal quality. Interference: Avoid placing the booster near objects that can cause interference, such as microwaves or thick walls, as this can reduce its effectiveness. Conclusion: In summary, while signal boosters can potentially work with various types of devices, their effectiveness depends on multiple factors including compatibility with the device's technology and frequency bands, as well as proper installation and placement. Always check the specifications of both your device and the booster before purchasing to ensure they are compatible and follow the manufacturer's guidelines for installation.

Is it safe to use a signal booster in my home or office ?
Signal boosters are devices that enhance cellular signals in areas where signal strength is weak. While they are commonly used in homes and offices to improve communication and connectivity, there are safety concerns associated with their use. These include potential increases in radiation exposure, interference with other electronic devices, and legal issues related to local regulations and carrier agreements. To use a signal booster safely, it is important to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully, position the booster away from other electronic devices, research local regulations and carrier agreements, monitor performance regularly, and maintain the device properly. By taking these precautions, you can help ensure that your signal booster remains safe and effective over time.

What is a signal booster and how does it work ?
A signal booster is a device that improves wireless signals in areas with weak coverage by receiving, amplifying, and retransmitting signals. It consists of an external antenna for capturing signals, a signal amplifier for increasing their power, and an internal antenna for distributing the enhanced signals. Benefits include improved reception, extended battery life, reduced dropped calls, increased coverage area, and healthier device performance. Signal boosters are useful in rural areas, basements, high-rise buildings, and vehicles traveling through challenging environments.

How do I choose the best signal booster for my needs ?
### How to Choose the Best Signal Booster for Your Needs When selecting a signal booster, consider factors such as your location, the type of signal you want to enhance, and the technology involved. Ensure compatibility with your network provider's frequency bands and your devices. Consider gain and range, legal requirements, installation and maintenance, budget, customer reviews, and brand reputation. Future-proof your choice by opting for upgradable systems.

How often should I replace or update my signal booster ?
This topic summary discusses the importance of maintaining and updating a signal booster to ensure optimal performance. It outlines signs that indicate it's time to replace the booster, such as decreased performance or physical damage. The text also emphasizes the significance of regular firmware updates for improved functionality and security. Additionally, it provides a step-by-step guide on how to update the firmware and offers maintenance tips to prolong the booster's lifespan, including cleaning antennas, avoiding obstructions, and regular inspections. Overall, the summary stresses the need for periodic checks and updates to keep the signal booster functioning effectively.

How do I install a signal booster in my building ?
Installing a signal booster in your building can improve mobile reception and internet connectivity. Identify problem areas, choose the right booster, determine antenna placement, run cables and connect boosters, test and adjust, and maintain and troubleshoot for optimal results.

How much does a good quality signal booster cost ?
Signal boosters, also known as cell phone signal amplifiers or repeaters, are electronic devices designed to improve the strength and reliability of cellular signals in areas with poor coverage. The cost of a good quality signal booster can vary depending on several factors such as the type of technology used, the frequency bands supported, the coverage area, and the brand. The main types of signal boosters are analog and digital, with analog boosters generally being less expensive but not as clear or strong as digital boosters. The more bands a booster supports, the higher the cost is likely to be. Larger coverage areas require more powerful boosters, which tend to be more expensive. Well-known brands often charge a premium for their products due to their reputation, customer service, and warranty offerings. The cost of a good quality signal booster generally ranges from $200 to $1000 USD. Basic signal boosters suitable for small areas like a single room or vehicle typically cost between $200 and $300 USD. Mid-range signal boosters offer moderate coverage areas suitable for apartments or small offices and generally fall within the $300 to $600 USD price range. High-end signal boosters provide extensive coverage for larger homes, buildings, or outdoor spaces and typically cost between $600 and $1000 USD. When purchasing a signal booster, it's essential to consider installation costs if you plan to hire a professional, as well as any potential shipping fees if buying online. Additionally, look for products that come with a warranty or guarantee to protect your investment over time.
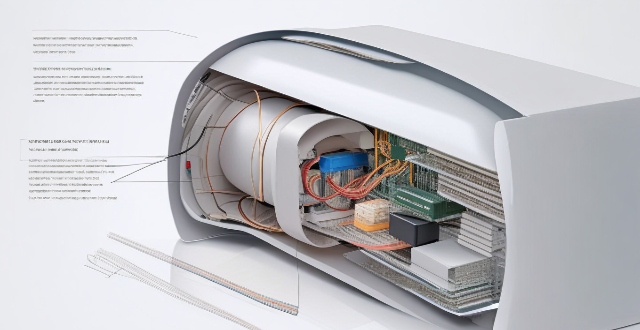
Are there any side effects of using a signal booster ?
Signal boosters can improve wireless connectivity but may cause side effects like overheating, interference with other devices, limited bandwidth, security concerns, and challenges from physical obstructions. It's important to consider these potential issues and take precautions to minimize them.
Why is my cell phone signal weak ?
The article discusses common reasons for weak cell phone signals, including distance from the cell tower, network congestion, device issues, and carrier-related problems. It suggests solutions such as moving closer to the cell tower, avoiding network congestion, checking device issues, and contacting your carrier to improve signal strength.

How do I choose a car charger for my device ?
When selecting a car charger for your device, consider factors such as compatibility with your device's charging port, charging speed, number of ports, additional features, reviews and ratings, budget, and brand reputation. By doing so, you can find a reliable and efficient car charger that meets your needs.

Can a signal booster be used outdoors ?
Signal boosters are versatile devices that can be used outdoors to enhance wireless signals like cellular, Wi-Fi, and GPS. While they offer significant advantages in improving connectivity in various outdoor scenarios, their effectiveness depends on factors such as environmental conditions and installation challenges. Proper planning and understanding of the specific needs and technical requirements are crucial for successful implementation.

How do I troubleshoot a faulty network connection device ?
This text provides a step-by-step guide on how to troubleshoot a faulty network connection device. It starts by identifying the problem, checking physical connections, restarting the device, checking network settings, updating firmware, checking for interference, and finally contacting support if all else fails. The text emphasizes the importance of patience and perseverance in troubleshooting technical issues.

Can I use Apple Music without an Apple device ?
The text discusses the availability of Apple Music across various platforms, including Windows, Android devices, web players, and smart TVs and streaming devices. It highlights the key features available on each platform and concludes that users don't need an Apple device to enjoy Apple Music.

How do I set up parental controls on my child's Apple device ?
The text provides a step-by-step guide on how to set up parental controls on an Apple device for children. The steps include creating a family group, turning on Screen Time, setting up content and privacy restrictions, establishing downtime and app limits, and monitoring the child's device usage. The purpose of these steps is to ensure the child's safety and well-being while using technology by controlling what apps, websites, and features they can access, as well as when and how much they can use their device.

How to use "Find My iPhone" to locate a missing device ?
The text provides a step-by-step guide on how to use the "Find My iPhone" feature to locate a missing Apple device. It emphasizes the importance of enabling the feature beforehand, signing in to iCloud, selecting the correct device, viewing its location on a map, and using additional features such as marking it as lost or erasing data remotely. It also suggests contacting local authorities if the device is believed to be stolen. Overall, it highlights the effectiveness of "Find My iPhone" in locating lost devices and protecting personal information.

How do I remove a device from my Apple account ?
Removing a device from your Apple account is a straightforward process that can be done in just a few steps. First, sign in to your Apple ID account page by going to [appleid.apple.com](https://appleid.apple.com) and entering your Apple ID and password. Then, view your devices by clicking on the "Devices" section. Choose the device you want to remove from the list of associated devices and click on it. To remove the device from your account, click on the "Remove" button. Confirm the removal in the pop-up window that appears. Finally, check your email for a confirmation message from Apple. Remember that removing a device from your account does not delete any data stored on the device itself; it only removes access to your Apple services such as iCloud and the App Store.

Can someone hack into my device through public Wi-Fi ?
Public Wi-Fi networks pose a significant risk to the security of your devices due to various types of attacks such as man-in-the-middle, eavesdropping, and malware distribution. To protect yourself from these threats, it is recommended to use a virtual private network (VPN), avoid accessing sensitive information on public Wi-Fi, keep your device up-to-date, use two-factor authentication, and be wary of rogue Wi-Fi networks. Following these tips can significantly reduce the chances of falling victim to hackers and protect your personal information from being stolen or compromised.

How do I know if a second-hand electronic device is still functional ?
Before buying a second-hand electronic device, it's important to check its functionality. Here are some steps you can take: visual inspection for physical damage, powering up the device, testing basic functions, checking battery life, connectivity tests, camera and microphone test, speaker and sound quality check, app testing, heat test, and resetting the device. By following these steps, you can make an informed decision about your purchase.

Is there a way to disable automatic updates in my Apple device ?
How to disable automatic updates in Apple device?

What are the benefits of using a GPS device for cycling routes ?
Using a GPS device for cycling routes offers benefits such as improved navigation, safety and security, performance tracking, and convenience. It provides accurate directions, real-time tracking, and the ability to save points of interest. Safety features include emergency alerts, night riding capabilities, and weather updates. Performance tracking measures speed, distance, elevation gain, and heart rate. Convenience is enhanced with no need for paper maps and automatic routing. Overall, using a GPS device can greatly enhance the cycling experience.

How can I improve my internet speed on public Wi-Fi ?
Improving internet speed on public Wi-Fi involves optimizing device settings, using online tools, and connecting to less congested networks. Tips include updating devices, turning off unnecessary apps, using a VPN, clearing browser cache, disabling extensions, using a lightweight browser, using a Wi-Fi booster or signal extender, avoiding peak times, choosing less popular networks, and testing speed with online tools like Speedtest and Google PageSpeed Insights.
**How often does iCloud back up my device, and can I control when it happens ?
iCloud backup is a feature that automatically backs up iOS devices to Apple's cloud storage service, ensuring data safety and restoration if needed. The frequency of these automatic backups depends on available iCloud space and device usage, typically occurring daily under specific conditions like Wi-Fi connection and device lock. Users can control when iCloud backup happens by manually initiating backups, turning off automatic backups, or adjusting backup settings.

How do I optimize my network connection device for video conferencing ?
Optimizing your network connection device for video conferencing is essential for a smooth and reliable communication experience. Here are some steps to follow: 1. Check Your Internet Speed: Test your connection speed and upgrade your plan if necessary. 2. Choose the Right Hardware: Use a wired Ethernet connection if possible, and ensure that your router and modem are up-to-date. 3. Optimize Your Network Settings: Set up Quality of Service (QoS) on your router and keep its firmware updated. 4. Minimize Interference: Reduce wireless interference and limit bandwidth usage during important video calls. 5. Use a Dedicated Network for Video Conferencing: Create a separate Virtual Private Network (VPN) or invest in business-grade networking solutions. By following these steps, you can optimize your network connection device for video conferencing, ensuring smooth and reliable communication with colleagues and clients around the world.

What is the purpose of a VPN (Virtual Private Network) device in a business network ?
The purpose of a VPN device in a business network is to provide secure and encrypted connections for remote access to the organization's resources, ensuring that employees, partners, and customers can access the company's data and applications securely from any location. Key features include encryption, authentication, firewall protection, scalability, and flexibility. Benefits of using a VPN device in a business network include enhanced security, improved productivity, cost savings, and simplified IT management.
**How can I access and manage my iCloud data from a non-Apple device ?
This guide provides step-by-step instructions on how to access and manage iCloud data from a non-Apple device. It includes prerequisites such as having an active iCloud account and using a compatible web browser. The steps include visiting the iCloud website, logging in to your account, choosing a service to access, managing your data, and signing out of iCloud when finished. Common actions within each service are also outlined. By following these steps, users can effectively access and manage their iCloud data from any non-Apple device with an internet connection and a compatible web browser.

How do I set up a VPN service on my computer or mobile device ?
Setting up a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is an excellent way to ensure your online privacy, bypass geo-restrictions, and enhance your security on the internet. Here's a detailed guide to setting up a VPN service on your computer or mobile device: 1. Choose a VPN Service Provider: Research and select a reliable VPN service that suits your needs in terms of security, speed, and price. Ensure the provider offers apps for your operating system, whether it's Windows, macOS, Android, or iOS. 2. Sign Up for the Service: Visit the VPN service website and sign up for an account. Choose a payment plan and complete the subscription process. 3. Download and Install the VPN App: Once you have subscribed, download the VPN app from your provider's website or your device's app store. Install the app on your device following the standard installation procedures. 4. Configure the VPN App: Open the VPN app and log in using your account credentials. Select a server location; usually, the app will recommend the fastest or closest server to you. Customize the settings if needed, such as enabling startup with Windows or configuring the kill switch feature. 5. Connect to the VPN: Click the connect button in the VPN app to establish a connection to the chosen server. A secure and encrypted tunnel will be created between your device and the server. 6. Verify the VPN Connection: Check your IP address and location using online services like `ipleak.net` to ensure your real identity is concealed. Test the connection by trying to access content that is normally blocked in your region. 7. Troubleshooting: If you encounter connection issues, check your network settings or try connecting to a different server. Make sure your firewall and antivirus software are not blocking the VPN connection. 8. Regular Maintenance and Updates: Keep your VPN app updated to benefit from the latest security features and performance improvements. Monitor your data usage if your VPN service has bandwidth limitations. Additional Considerations: Look for VPN services that offer strong encryption protocols like OpenVPN or IKEv2 for maximum security. Ensure that your VPN service has a strict no-logs policy to protect your online activities from being recorded. Some VPN services allow multiple devices to be connected simultaneously under one account – consider this feature if you use multiple devices.

How do I boost my cell phone signal strength ?
Having a strong cell phone signal is crucial for making calls, sending messages, and using mobile data. If you're experiencing poor signal strength, there are several ways to improve it. Here are some tips on how to boost your cell phone signal strength: 1. Check for Obstructions: Objects like buildings, walls, and trees can block or weaken signals. Try moving to an area with fewer obstructions. 2. Use 2G Instead of 3G/4G: If you're having trouble with 3G or 4G, switch to 2G. While slower, 2G networks are more widespread and often provide better coverage in remote areas. 3. Keep Your Phone's Software Up to Date: Manufacturers often release updates that can improve signal strength. 4. Use a Signal Booster: These devices work by capturing an outside signal, amplifying it, and rebroadcasting it inside your home or office. They can significantly improve signal strength in areas with weak coverage. 5. Contact Your Service Provider: If none of the above solutions work, contact your service provider and report the issue. They may be able to identify a problem with their network or offer additional solutions.

How do I safely dispose of old or damaged electrical devices ?
This comprehensive guide outlines steps for safely disposing of old or damaged electrical devices, including identifying the type of device, checking with the manufacturer, contacting local authorities and recycling centers, donating or selling still-functional devices, properly packaging and transporting devices, considering environmental impacts, and avoiding harmful disposal methods.

How do I manage storage space on my Apple device ?
Managing Storage Space on Your Apple Device Checking Storage Space: - Open Settings and tap General. - Select iPhone Storage (or iPad/iPod Storage). - View a bar graph showing used and available storage, and a list of apps sorted by storage usage. Tips for Managing Storage Space: 1. Delete Unused Apps: Remove apps from the Home Screen or through Settings to free up space. 2. Offload Unused Apps: Enable Offload Unused Apps in Settings to remove apps while keeping their data. 3. Optimize Photo Storage: Use Optimized Storage in Photos settings and manually delete unwanted photos/videos. 4. Clear App Cache and Data: Offload apps to keep their data and reinstall them to remove it. 5. Use Cloud Services: Back up to iCloud and store files in iCloud Drive to save local storage. 6. Manage Messages: Auto-delete old messages and review attachments before deleting conversations. 7. Manage Media and Downloads: Stream content instead of downloading and delete downloaded episodes and songs. 8. Other Tips: Regularly check storage, disable auto downloads, and consider resetting your device if needed.