Gasoline hybrid vehicles, known as HEVs, merge an ICE with an electric motor for enhanced efficiency and reduced emissions. Key components include the ICE, electric motor, battery pack, transmission, and a generator/alternator. These cars can operate in various modes: fully on ICE power, purely electric, combined power, or through regenerative braking. The energy management controller optimizes power distribution for peak efficiency. Benefits of gasoline hybrids include better fuel economy, lower emissions, extended brake life, and potential tax incentives.
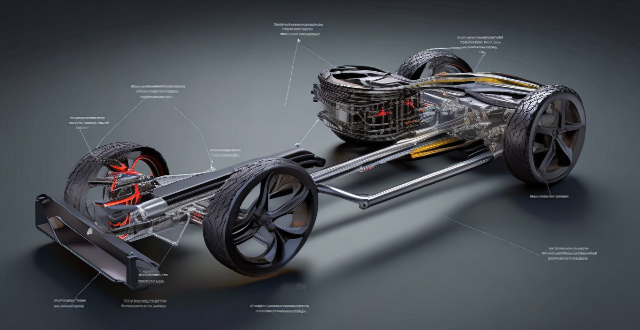
How Does a Gasoline Hybrid Car Work?
A gasoline hybrid car, also known as a hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), combines a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor to achieve better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions compared to conventional gasoline-powered cars. Here's a detailed explanation of how a gasoline hybrid car works:
Powertrain Components
The powertrain of a gasoline hybrid car typically includes the following components:
- Internal Combustion Engine (ICE): A standard gasoline engine that provides power for the vehicle.
- Electric Motor: An electric motor that can propel the vehicle on its own or assist the ICE.
- Battery Pack: A set of batteries that store energy for the electric motor.
- Transmission: A mechanism that transfers power from the ICE and/or electric motor to the wheels.
- Generator/Alternator: A device that recharges the battery pack using excess energy from the ICE or through regenerative braking.
Operating Modes
Gasoline hybrid cars operate in several modes depending on driving conditions:
- Full ICE Power: When more power is needed, such as for acceleration or climbing hills, the ICE takes over and powers the vehicle.
- Full Electric Power: At low speeds or during light acceleration, the electric motor can drive the vehicle on its own, using energy stored in the battery pack.
- Combined Power: During moderate driving conditions, both the ICE and electric motor work together to provide optimal efficiency and performance.
- Regenerative Braking: When decelerating or braking, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy to recharge the battery pack.
Energy Management
The hybrid system's energy management controller (EMC) continuously monitors driving conditions and adjusts power distribution between the ICE and electric motor accordingly. This ensures that the vehicle operates at peak efficiency by utilizing the most appropriate source of power for each situation.
Benefits of Gasoline Hybrid Cars
Gasoline hybrid cars offer several benefits over traditional gasoline-only vehicles:
- Improved Fuel Economy: By combining an electric motor with an ICE, hybrid cars achieve higher fuel economy than their non-hybrid counterparts.
- Reduced Emissions: Hybrid cars produce fewer emissions overall due to their increased efficiency and the use of regenerative braking.
- Regenerative Braking: This feature helps to extend the life of brake pads and reduces wear on the brake system.
- Tax Incentives and Rebates: Some governments offer incentives for purchasing hybrid vehicles, which can help offset their typically higher purchase price compared to conventional cars.
In summary, a gasoline hybrid car utilizes a combination of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor to provide power while maximizing fuel efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. The sophisticated energy management system within these vehicles allows them to seamlessly transition between different operating modes based on driving conditions, offering a practical solution for those looking to reduce their carbon footprint without sacrificing performance or convenience.