Performance Function

How does hydration impact athletic performance and health ?
Hydration is crucial for athletic performance and health. Adequate hydration maintains energy levels, muscle function, joint lubrication, heart rate, and cognitive function during exercise. Dehydration can lead to fatigue, muscle cramping, increased heart rate, impaired cognitive abilities, and decreased physical performance. Proper hydration also aids digestion, kidney function, skin health, immune system function, and body temperature regulation. Chronic dehydration can increase the risk of kidney stones, digestive issues, weakened immune system, and other health problems. Therefore, it is essential for athletes to stay well-hydrated to achieve optimal performance levels and support their overall health.

Can certain vitamins improve athletic performance ?
Vitamins play a crucial role in various bodily functions, including metabolism, immunity, and tissue repair. Athletes often seek to optimize their performance by ensuring they have adequate vitamin intake. Certain vitamins like B-complex, Vitamin D, Vitamin C, and vitamins A, C, and E can improve athletic performance by supporting energy metabolism, muscle function, recovery, and immunity. However, it's essential to ensure an adequate intake through a balanced diet and consider supplementation only when necessary and under professional guidance. The key is to find the right balance that works for each individual athlete's unique needs and circumstances.
How does exercise improve cognitive function ?
Exercise plays a crucial role in enhancing cognitive function, including memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. It promotes brain plasticity, increases blood flow and oxygenation, reduces inflammation, and improves sleep quality. Incorporating exercise into your routine can be done through various activities such as running, swimming, or yoga. Start small and gradually increase intensity and duration, find enjoyable activities, incorporate mindful movement, make it social, set realistic goals, and consult with a professional if needed.

Is there a link between physical fitness and cognitive function ?
The text discusses the potential link between physical fitness and cognitive function, citing research that suggests a correlation. It defines physical fitness as the ability to perform aspects of sports or occupations, obtained through proper nutrition, exercise, and rest, and cognitive function as mental processes involving perceiving, remembering, reasoning, problem-solving, understanding, judging, and learning. The text mentions studies that suggest enhanced physical fitness can improve cognitive function in older people without known cognitive impairment and that physical fitness could be a better predictor of cognitive performance than physical activity. It also discusses potential mechanisms behind the relationship, including increased blood flow to the brain and the release of chemicals that promote cell growth, improvement, and survival. Finally, it notes the potential implications of this research for individual and societal health.

Does exercise have different effects on cognitive function at different ages ?
This article explores the relationship between exercise and cognitive function across various age groups. It highlights the benefits of exercise for children's cognitive development, adults' reduced risk of cognitive decline, and older adults' slowed cognitive decline. Examples of suitable exercises for each age group are provided, including playing sports for children, aerobic activities for adults, and walking or cycling for older adults. The article concludes that incorporating physical activity into daily routines at any age is crucial for maintaining cognitive health and overall well-being.

Is there a relationship between exercise and cognitive function ?
Exercise is a potential intervention for enhancing cognitive function across the lifespan. The relationship between exercise and cognitive function is complex and multifaceted, involving various aspects of cognition and different types of exercise. Long-term exercise interventions have consistently shown positive effects on cognitive function, particularly in older adults. Different types of exercise may influence specific cognitive functions differently, and the underlying mechanisms behind these effects are still being explored. By incorporating regular physical activity into our daily routines, we can potentially enhance our cognitive function and overall well-being.

How long after starting an exercise routine can improvements in cognitive function be expected ?
The text discusses the timeline for improvements in cognitive function after starting an exercise routine. It mentions that immediate benefits such as enhanced mood, improved attention and focus, and increased energy levels can be noticed within 1-3 months. Mid-term benefits like enhanced memory retention, improved executive function, and increased creativity can be observed within 3-6 months. Long-term benefits such as slowed cognitive decline, reduced risk of cognitive disorders, and sustained improvements in overall cognitive performance can be achieved after six months or longer. The text emphasizes the importance of maintaining a consistent exercise regimen over the long term for sustained enhancements in various aspects of cognitive function.

What role does exercise play in maintaining cognitive function in old age ?
Exercise is crucial for maintaining cognitive function in old age, with benefits including improved blood flow, reduced inflammation, and increased neuroplasticity. Aerobic exercise, resistance training, and activities like yoga and tai chi are all beneficial. Incorporating physical activity into your daily routine can help keep your mind sharp as you age.

Is there a specific duration or intensity of exercise needed to improve immune function ?
The relationship between exercise and immune function is complex, but research suggests that regular physical activity can enhance the immune system. However, both the duration and intensity of exercise play significant roles in achieving this beneficial effect. The American Heart Association recommends at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity per week for adults. Engaging in prolonged periods of endurance exercise can temporarily suppress immune function due to increased stress on the body. Light activities like walking or yoga can still offer immune benefits by reducing stress and promoting overall health. Regular moderate to high-intensity exercises, such as jogging, cycling, or strength training, are generally considered optimal for enhancing immune function. Adequate rest and recovery are crucial for maintaining a healthy immune system. Combining different types of exercises (aerobic, strength training, flexibility work) can provide a well-rounded approach to enhancing immune function. Staying hydrated and consuming a balanced diet rich in nutrients supports both exercise performance and immune health. Other lifestyle habits, including sleep quality, stress management, and avoidance of harmful substances, also play a vital role in supporting immune function alongside exercise.

Can napping improve athletic performance ?
**Can Napping Improve Athletic Performance?** Napping is a common practice among athletes and non-athletes alike, but can it really improve athletic performance? Research suggests that napping can aid in physical recovery and enhance cognitive function. Physical Recovery: - **Muscle Repair**: Sleep produces growth hormone, aiding in muscle repair and growth. - **Reduced Inflammation**: Sleep reduces inflammation, leading to better recovery after exercise. Cognitive Function: - **Improved Focus**: A quick nap can improve focus and concentration for peak performance. - **Enhanced Learning**: Sleep consolidates memories, allowing athletes to learn from mistakes and improve skills faster. Effective Napping Tips: Timing: - **Power Naps**: Limit naps to 20-30 minutes to avoid deep sleep and feeling groggy upon waking. - **Timing Before Bedtime**: Avoid napping too close to bedtime to prevent disrupting the nighttime sleep cycle. Environment: - **Quiet and Dark**: Find a quiet, dark place to nap for better sleep quality. - **Comfortable Surface**: Choose a comfortable surface to prevent waking up with aches and pains. In conclusion, napping can improve athletic performance by aiding physical recovery and enhancing cognitive function. It's important to nap effectively by timing your naps appropriately and creating a comfortable environment.
Can you explain the function of a network switch in a home network setup ?
The article discusses the function of a network switch in a home network setup. The primary function of a network switch is to connect multiple devices together, either through Ethernet cables or wireless connections. It also manages data traffic within the network by forwarding data packets to their intended destination based on their IP address. Additionally, network switches enhance network performance by providing dedicated bandwidth to each connected device and prioritizing certain types of traffic over others. Finally, network switches come with various security features that help protect your home network from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Can nutrition affect an athlete's skill level ?
Nutrition is vital for athletes' overall well-being and performance, including skill enhancement, recovery, and injury prevention. It affects cognitive function, physical performance, and recovery, ultimately influencing an athlete's skill level. A balanced diet with proper nutrients can help athletes reach their full potential and succeed in their sports.
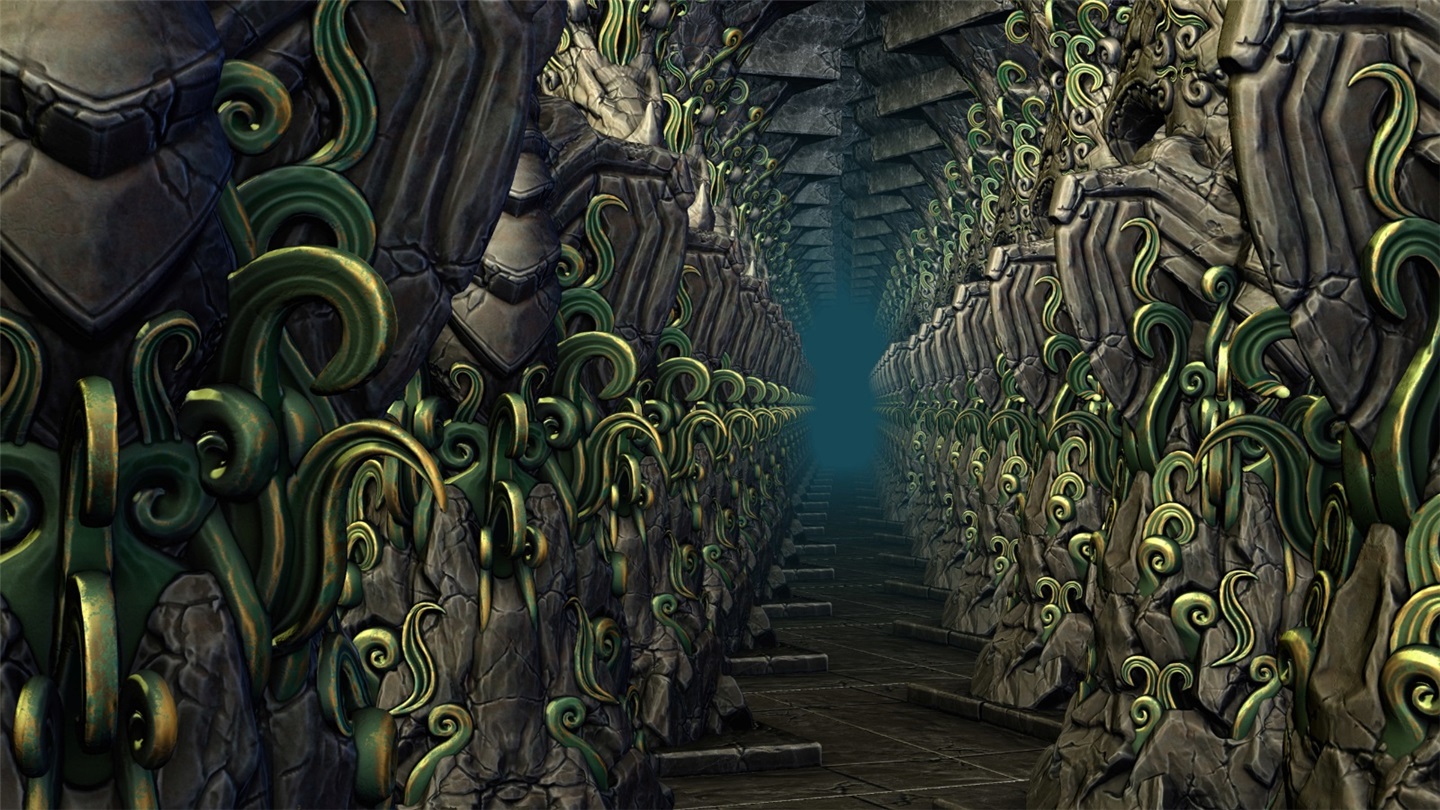

In 3D graphics, mesh is a set of vertices, edges and faces that define the shape of an object. In the current drawing pipeline, all geometric data in the mesh must be processed sequentially before any other steps can be taken. This can be a major performance bottleneck.
The mesh shader replaces the old pattern with a new geometric processing method, which simplifies the graphics pipeline and provides developers with greater flexibility and control. Mesh shaders can process some segments of the mesh in parallel, called "mesh segments", with a greater degree of flexibility and control.

Users need to update 3dmark software to the latest version, and you can see this option in the "function test" area below the test list. In addition, there are DirectX ray tracing function test, PCI Express function test and so on.
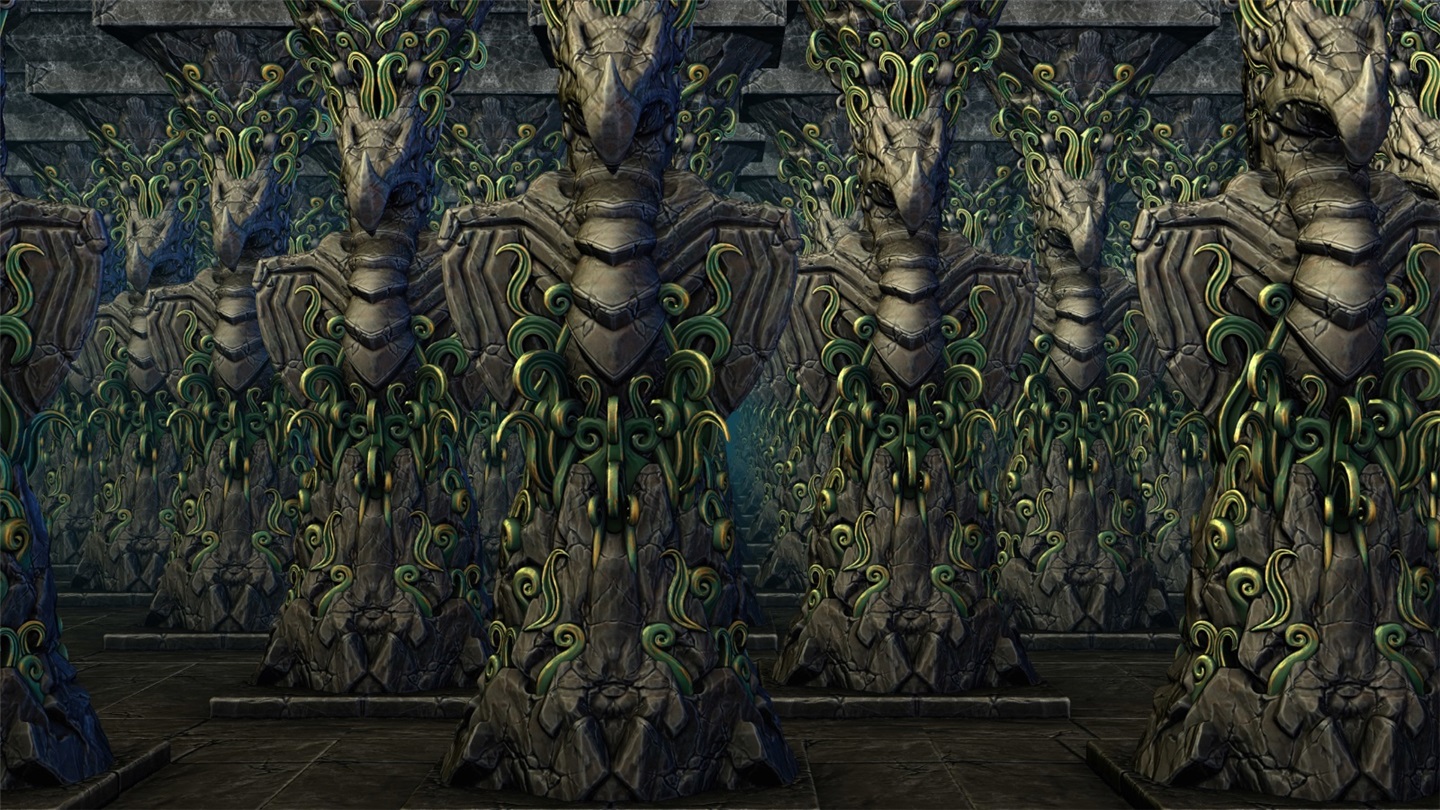
The 3dmark mesh shader function test will show you how the game engine can effectively eliminate the invisible geometry of the camera using the mesh shader pipeline, so as to improve the performance of the game.
The test scenario is a hall containing many rows of carved columns with high fineness. When the camera moves in the scene, the columns in the foreground block the scenery behind.
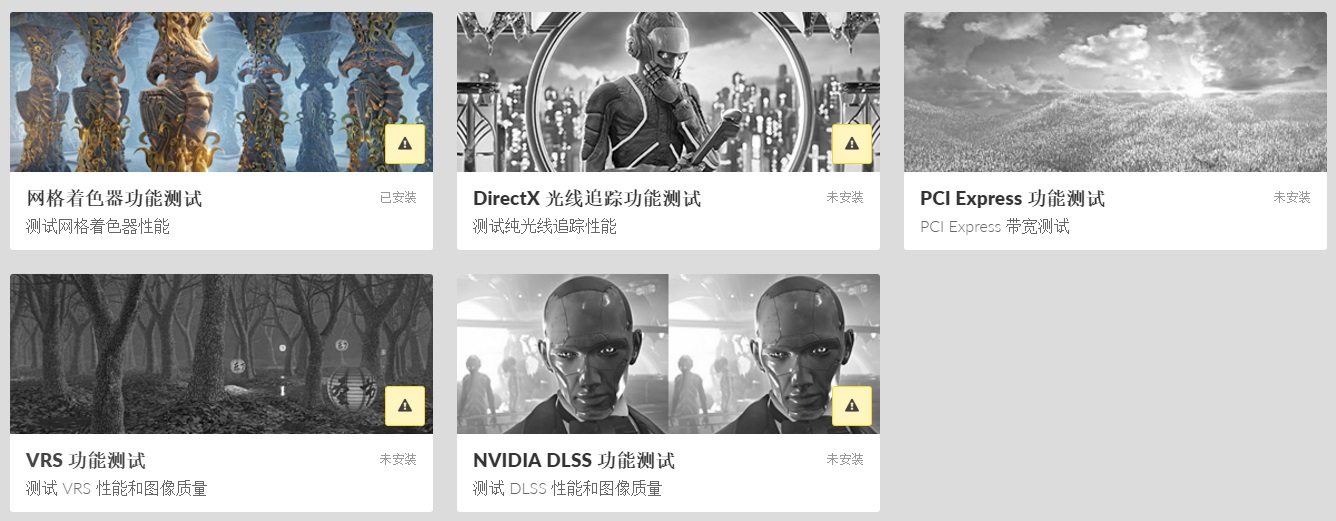
The 3dmark mesh shader function test includes an interactive mode that can help you intuitively see the benefits of using mesh shaders. You can pause and jump to different parts of the timeline and change settings in real time. Use the visualizer options to highlight mesh clips, or view the level of detail (LOD) used by each mesh clip.
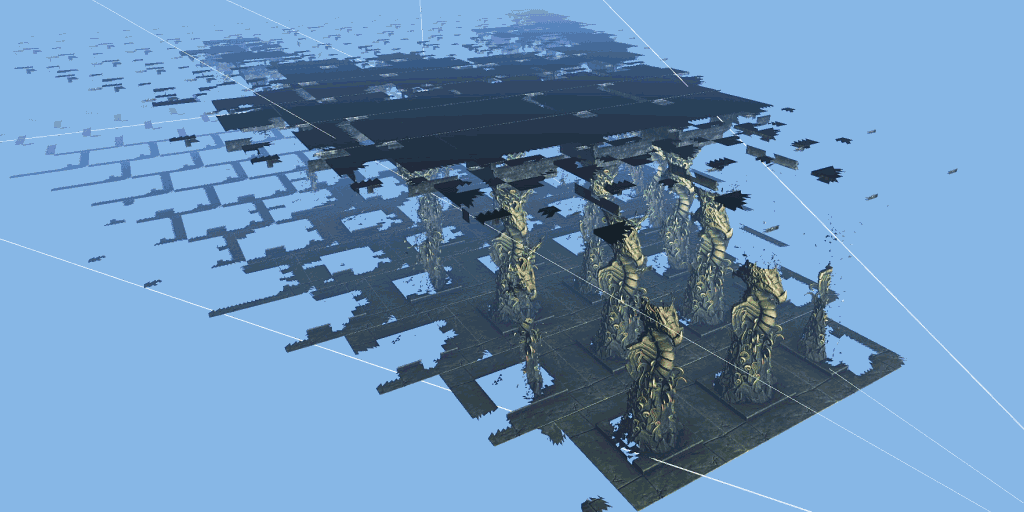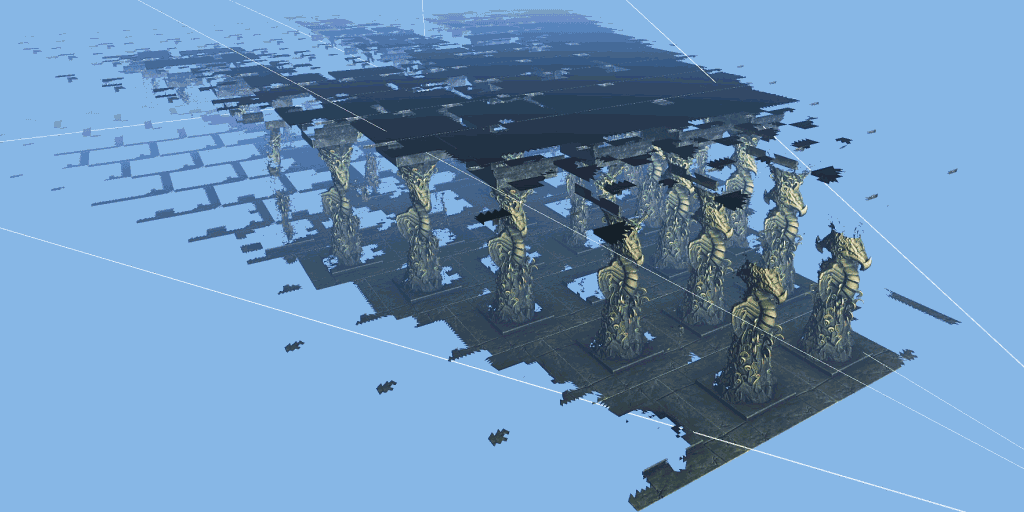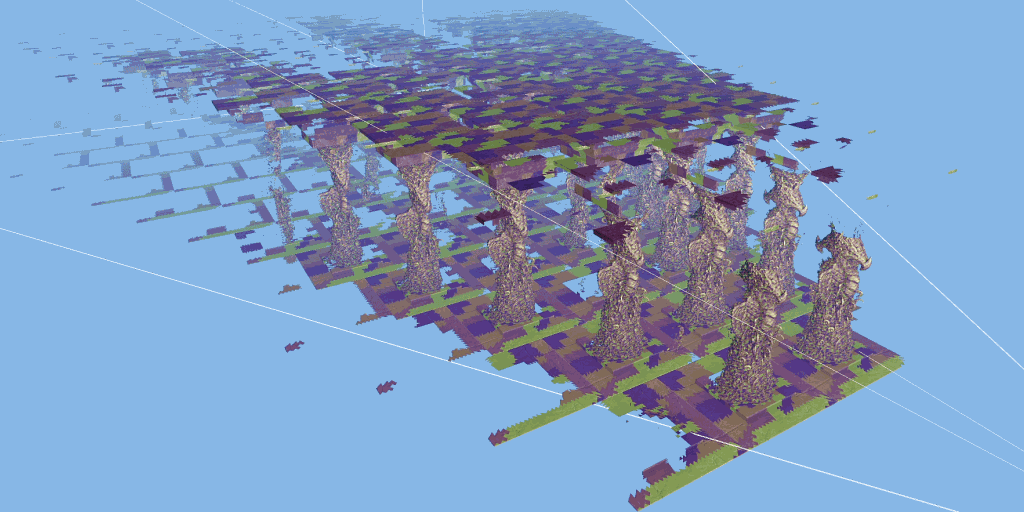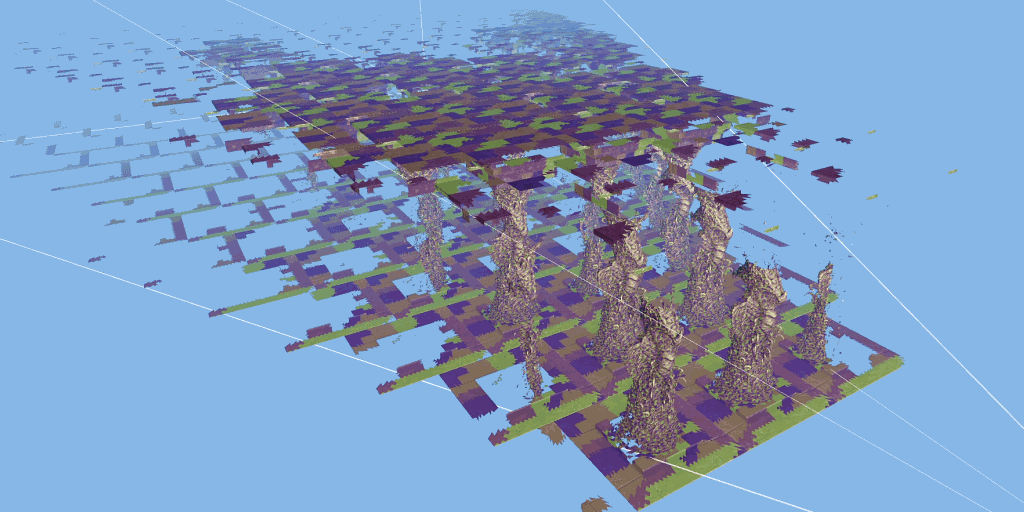
Major update of 3dmark: the function test of mesh shader can be carried out, and dx12 ultimate needs to be supported

How does lack of sleep impact athletic performance ?
The text discusses the importance of sleep for athletes, explaining that adequate sleep is essential for muscle recovery and repair, cognitive function, and regulation of energy levels. Lack of sleep can negatively impact athletic performance by decreasing endurance, impairing reaction time and coordination, increasing the risk of injury, altering mood and mental health, and reducing motivation and focus during training or competition. The article concludes that prioritizing sleep as part of an athlete's overall training regimen is crucial for optimal performance.

How does exercise influence neuroplasticity and cognitive function ?
Exercise has a positive impact on neuroplasticity and cognitive function by increasing blood flow, releasing growth factors, reducing inflammation, improving attention and concentration, enhancing memory, and slowing cognitive decline. Incorporating regular physical activity into your lifestyle can have numerous benefits for your brain health and overall well-being.

How does aerobic exercise impact lung capacity and function ?
Aerobic exercise can increase lung capacity and improve lung function by strengthening the muscles used for breathing, stimulating the respiratory system, and increasing gas exchange efficiency. Regular aerobic exercise can also reduce the risk of respiratory diseases, improve immune function, and reduce inflammation in the airways.

How does dehydration during exercise affect performance and physiological responses ?
Dehydration during exercise can significantly impact performance and physiological responses. It decreases blood volume, impairs thermoregulation, affects cognitive function, increases heart rate and blood pressure, causes respiratory alkalosis, leads to muscle cramping and stiffness, and alters metabolic processes. Athletes should stay hydrated to avoid these negative effects.

What is the relationship between exercise physiology and nutrition for athletes ?
The article discusses how exercise physiology and nutrition are interconnected for athletes, with each influencing the other. It defines exercise physiology as the scientific study of how the body functions during physical activity, covering areas like energy systems, muscle function, cardiovascular responses, respiratory functions, and thermoregulation. Nutrition for athletes involves strategic eating plans to enhance performance, aid recovery, and maintain overall health, focusing on macronutrients, micronutrients, hydration, and timing of intake. The intersection of these two aspects includes fueling performance, recovery and repair, hydration and thermoregulation, energy balance, supplementation, and dietary needs variation. A comprehensive understanding of both exercise physiology and nutrition is crucial for athletes to achieve peak performance.

How does sleep quality affect athletic performance and health ?
This text explains how sleep quality affects athletic performance and overall health. It emphasizes the importance of sleep for physical recovery, mental well-being, and immune system support in athletes. Poor sleep quality can lead to decreased performance, increased injury risk, and mental health issues. The text provides tips for improving sleep quality, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule and creating a comfortable sleep environment. Adequate sleep is crucial for optimal athletic performance and overall health.

Can exercise compensate for poor sleep quality in terms of cognitive function ?
The article discusses the importance of sleep for cognitive function and whether exercise can compensate for poor sleep quality. While exercise has benefits for cognitive function, it cannot fully replace the memory consolidation and emotion processing that occurs during sleep. Chronic sleep deprivation can lead to long-term changes in brain structure and function that may not be reversible through exercise alone. To maintain optimal cognitive function, both regular physical activity and good sleep habits are essential.

What kind of food and drinks should I consume to enhance my performance during exams ?
Proper nutrition is vital for exam performance, helping to maintain focus and energy. Recommended brain-boosting foods include lean proteins, complex carbohydrates, healthy fats, and antioxidant-rich items. Hydration is also key, with a suggestion to avoid sugary drinks and excessive caffeine. Meal ideas provide balanced options for breakfast, lunch, snacks, and dinner, emphasizing the importance of consistent healthy eating habits in the lead-up to exams.
How does exercise affect brain function and cognitive abilities ?
This article discusses how regular physical activity positively impacts brain function and cognitive abilities by improving blood flow, boosting neurotrophic factors, enhancing plasticity, and reducing inflammation. It emphasizes the importance of incorporating exercise into one's lifestyle for maintaining and enhancing cognitive health.

What is the relationship between sleep and recovery in high-level sports performance ?
Sleep is a vital component of recovery for high-level athletes, playing a significant role in muscle repair, energy restoration, immune function, cognitive function, and emotional well-being. Optimal sleep can lead to improved performance, reduced injury risk, enhanced learning and adaptation, increased motivation and focus, and better weight management. To maximize the benefits of sleep for recovery, athletes should establish good sleep habits such as maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a conducive sleep environment, limiting caffeine and alcohol intake, practicing relaxation techniques, and avoiding naps or keeping them short and early in the day.

What are the best sports nutrition supplements for enhancing athletic performance ?
The article discusses the importance of sports nutrition supplements in enhancing athletic performance. It highlights five key supplements that can help athletes improve their performance: 1. Protein Supplements: Essential for building and repairing muscles, protein supplements like whey, casein, and soy protein can support muscle growth, increase strength, and improve body composition. 2. Creatine Supplements: Popular among athletes for increasing muscle mass and improving performance during short, high-intensity exercise. Creatine also enhances recovery between workouts. 3. Beta-Alanine Supplements: An amino acid that increases muscle carnosine levels, beta-alanine can improve endurance capacity during high-intensity exercise, reduce fatigue, and enhance muscle strength and power. 4. Caffeine Supplements: A natural stimulant that can increase energy levels, reduce fatigue, improve mental focus, and enhance endurance capacity during prolonged exercise. 5. Multivitamins and Minerals Supplements: Important for overall health and well-being, multivitamins and minerals can help prevent nutrient deficiencies that could impair performance and enhance immune function and recovery from training. The article emphasizes the importance of choosing safe and effective supplements that meet the specific needs of an athlete and consulting with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian before starting any new supplement regimen.

How can nutrition affect an athlete's performance ?
Nutrition plays a pivotal role in an athlete's performance, providing essential energy, aiding recovery, and maintaining overall health. A balanced intake of macronutrients, such as carbohydrates for immediate energy, proteins for muscle repair and growth, and fats for long-term energy, is crucial. Micronutrients like vitamins and minerals also contribute to metabolic functions and electrolyte balance. Hydration is vital for fluid balance and preventing performance decline due to dehydration. Timing of nutrient intake, before, during, and after exercise, significantly impacts performance and recovery. Strategic dietary planning, including periodized nutrition and anti-doping compliance, ensures athletes meet their specific needs and maintain clean sport standards. Overall, a well-structured nutritional plan can enhance athletic performance and success in sports.